Overview
The Degree algorithm calculates the number of edges for each node, and the sum of weights when there are weights on the edges. Since it is a shallow (≤ 1 layer) calculation for nodes, degree is the simplest and most efficient graph algorithm, which plays a vital role in scientific computing, feature extraction, supernode recognition and other fields.
Basic Concept
Degree Direction
The number of outbound edges of node is called out degree of the node; conversely, the number of inbound edges of node is called in degree of the node. If ignores the direction of edges, that is degree (or degree centrality) of the node.
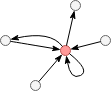
Out degree of the red node in the graph above is 3, in degree is 4, degree is 7. Please note that the directed self-loop edge is regarded as an outbound edge and an inbound edge.
Edge Weight
Edge weight can be a property value of edge. When edge weights are specified, degree is the sum of all edge weights. The degree of node without specifying any edge weight can be viewed as the degree when all edge weights are 1.
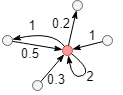
After the edges are weighted, out degree of the red node in the graph above is 1 + 0.2 + 2 = 3.2, in degree is 0.5 + 0.3 + 2 + 1 = 3.8, degree is 3.2 + 3.8 = 7.
Special Case
Lonely Node, Disconnected Graph
The degree of lonely node only depends on its self-loop edge because it has no edge connected to other nodes.
Self-loop Edge
Self-loop edge is regarded as an outbound edge and an inbound edge.
Directed Edge
The direction of directed edge is the basis for calculating out degree and in degree; the direction of edge is ignored when calculating degree.
Results and Statistics
Take this small social network of 8 users as an example, nodes represent users, edges represent relationship of follow, the weight on each edge is from the property score:
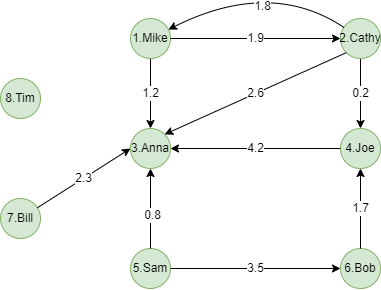
Algorithm results: Calculate weighted degree for each node, return _id, degree or _uuid, degree according to the execution method
| _uuid | _id | degree |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mike | 4.9 |
| 2 | Cathy | 6.5 |
| 3 | Anna | 11.1 |
| 4 | Joe | 6.1 |
| 5 | Sam | 4.3 |
| 6 | Bob | 5.2 |
| 7 | Bill | 2.3 |
| 8 | Tim | 0 |
Algorithm statistics: Total degree total_degree and average degree average_degree
| total_degree | average_degree |
|---|---|
| 40.4 | 5.05 |
Command and Configuration
- Command:
algo(degree) - Configurations for the parameter
params():
| Name | Type | Default |
Specification | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ids / uuids | []_id / []_uuid |
/ | / | IDs or UUIDs of nodes to be calculated; all nodes to be calculated if not set |
| edge_schema_property | []@<schema>?.<property> |
/ | Numeric edge property; LTE needed; schema can be either carried or not | Edge weight property/properties; edge without any specified property does not participate in the calculation; degree is unweighted if not set |
| direction | string | / | in/out, case insensitive | Edge direction; direction ignored if not set |
| limit | int | -1 | >=-1 | Number of results to return; return all results if sets to -1 |
| order | string | / | ASC/DESC, case insensitive | To sort the returned results; no sorting is applied if not set |
Algorithm Execution
Task Writeback
1. File Writeback
| Configuration | Data in Each Row |
|---|---|
| filename | _id,degree |
Example: Calculate degree of all nodes, write the algorithm results back to file
algo(degree).params().write({
file:{
filename: "degree_all"
}
})
2. Property Writeback
| Configuration | Writeback Content | Type | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| property | degree |
Node property | int64 when edge is unweighted, int64 or double when edge is weighted |
Example: Calculate weighted degree of all nodes, write the algorithm results back to node property
algo(degree).params({
edge_schema_property: @follow.score
}).write({
db:{
property: "degree"
}
})
3. Statistics Writeback
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
total_degree |
float | Total degree of all nodes |
average_degree |
float | Average degree of all nodes |
Example: Calculate degree of all nodes, write the algorithm statistics back to task information
algo(degree).params().write()
Direct Return
Alias Ordinal |
Type |
Description |
Column Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | []perNode | Node and its degree | _uuid, degree |
| 1 | KV | Total and average degree of all nodes | total_degree, average_degree |
Example: Calculate weighted degree of all nodes, return the results and statistics, order the results in the descending degree
algo(degree).params({
edge_schema_property: @follow.score,
order: "desc"
}) as results, stats
return results, stats
Streaming Return
Alias Ordinal |
Type |
Description |
Column Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | []perNode | Node and its degree | _uuid, degree |
Example: Find 1-hop neighbors of the node with the highest degree, return all information of those neighbors
algo(degree).params({
order: "desc",
limit: 1
}).stream() as results
khop().src({_uuid == results._uuid}).depth(1) as neighbors
return neighbors{*}
Real-time Statistics
Alias Ordinal |
Type |
Description |
Column Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | KV | Total and average degree of all nodes | total_degree, average_degree |
Example: Calculate out degree of all nodes, return the statistics
algo(degree).params({
direction: "out"
}).stats() as stats
return stats

