✓ File Writeback ✓ Property Writeback ✓ Direct Return ✓ Stream Return ✕ Stats
Overview
The K-Hop All algorithm identifies the neighborhood of each node within a graph. This algorithm finds extensive application in various scenarios, including relationship discovery, impact prediction, and friend suggestion.
The K-Hop All algorithm can be considered as the batch execution of the UQL K-Hop Query.
Considerations
Although the K-Hop All algorithm is optimized for high concurrency performance, it is important to note that this algorithm may require significant computational resources when dealing with large graphs (those with tens of millions of nodes or edges), or graphs containing many super nodes. To optimize performance, it is advisable to avoid performing K-Hop All calculation that is excessively deep, considering the specific characteristics and size of the graph being analyzed.
In graph G = (V, E), if |V|/|E|=100, querying the 5-hop neighbors of a node requires a theoretical computational complexity of 105 (equivalent to 10 billion computations), which would take approximately 100ms. Extrapolating from this, completing such a query in a graph with 10 million nodes would require 1 million seconds (equivalent to around 12 days). It's important to consider the computational demands and time requirements when working with graphs of this scale.
Syntax
- Command:
algo(khop_all) - Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ids / uuids | []_id / []_uuid |
/ | / | Yes | ID/UUID of the target nodes to perform k-hop queries, target all nodes if not set |
| k_start | int | >= 1 | 1 |
Yes | Starting depth of the k-hop query, the querying depth is [k_start, k_end] |
| k_end | int | >= 1 | 1 |
Yes | Ending depth of the k-hop query, the querying depth is [k_start, k_end] |
| direction | string | in, out |
/ | Yes | All edge directions in the querying path |
| node_property | []@<schema>?.<property> |
Numeric type, must LTE | / | Yes | Node properties to perform aggregations; this option must be used with aggregate_opt |
| aggregate_opt | []string | max, min, mean, sum, var, dev |
/ | Yes | The aggregation methods to perform on the values of the specified node properties; this option must be used with node_property, with each method corresponds to one propertymax: maximum, min: minimum, mean: average, sum: sum, var: variance, dev: standard deviation |
| src_include | int | 0, 1 |
0 |
Yes | 1 means to include every target node in its querying and aggregation results, 0 means not to include |
| limit | int | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Number of results to return, -1 to return all results |
Examples
The example is a transaction network between bank cards:
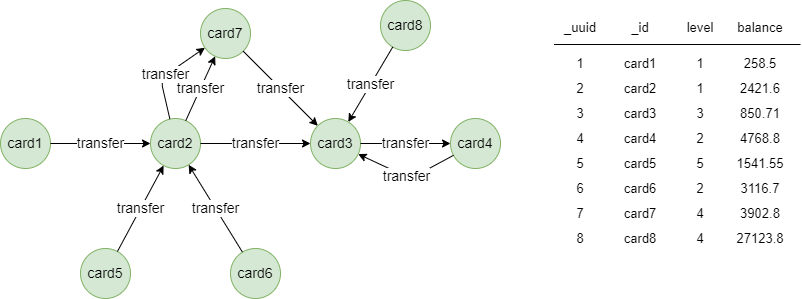
File Writeback
Spec |
Content | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filename_ids | _id,_id |
The first _id represents the target node, the second _id represents the neighbor of the target node |
| filename | _id,aggregate_result1,...,aggregate_resultN,count |
_id represents the target node, aggregate_result1 ~ aggregate_resultN are the aggregation results, the last count is the total number of neighbors of the target node |
algo(khop_all).params({
ids: ['card1', 'card7'],
k_start: 2,
k_end: 3,
direction: 'out',
node_property: ['@card.level', '@card.balance'],
aggregate_opt: ['max', 'mean']
}).write({
file:{
filename_ids: 'neighbors',
filename: 'aggregations'
}
})
Results: Files neighbors, aggregations
card1,card7
card1,card3
card1,card4
card7,card4
card1,4.000000,3174.103333,3.000000,
card7,2.000000,4768.800000,1.000000,
Property Writeback
| Spec | Content | Write to | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| property | Number of neighbors | Node property | double |
algo(khop_all).params({
k_start: 2,
k_end: 2
}).write({
db:{
property: 'khop2'
}
})
Results: The number of 2-hop neighbors of each node is written to a new property named khop2
Direct Return
| Alias Ordinal | Type | Description |
Columns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | []perNode | Node and its aggregation results, and number of neighbors | _uuid, value |
algo(khop_all).params({
ids: ['card1', 'card7'],
k_start: 2,
k_end: 3,
node_property: ['@card.level', '@card.balance'],
aggregate_opt: ['max', 'mean']
}) as r
return r
Results: r
| _uuid | value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 5.000000,6884.060000,6.000000, |
| 7 | 5.000000,7361.870000,5.000000, |
Stream Return
| Alias Ordinal | Type | Description |
Columns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | []perNode | Node and its aggregation results, and number of neighbors | _uuid, value |
algo(khop_all).params({
uuids: [2],
k_start: 2,
k_end: 2,
node_property: '@card.balance',
aggregate_opt: 'max'
}).stream() as results
return results
Results: results
| _uuid | value |
|---|---|
| 2 | 27123.800000,2.000000, |

