Overview
The FILTER statement allows you to discard records in the intermediate result table that do not satisfy the specified conditions.
<filter statement> ::= "FILTER" [ "WHERE" ] <search condition>
The FILTER and FILTER WHERE behave the same way. The use of WHERE in this context is often a matter of style or readability. For example:
MATCH (n:User)
FILTER n.age > 25
RETURN n
is functionally identical to:
MATCH (n:User)
FILTER WHERE n.age > 25
RETURN n
In both cases, the FILTER statement returns nodes where the user's age is greater than 25.
FILTER vs. MATCH WHERE
The FILTER statement and the WHERE clause are both used to apply filtering conditions in queries, but they differ in when and how they are evaluated.
The WHERE is a clause that can only be used with the MATCH statement. It can appear inside node or edge patterns, or directly after the list of path patterns, and is evaluated as part of the graph pattern matching process.
MATCH (n:User)
WHERE n.age > 25
RETURN n
FILTER is a standalone statement that offers greater flexibility and can be used wherever needed within a query.
MATCH (n:User)
FILTER n.age > 25
RETURN n
Example Graph
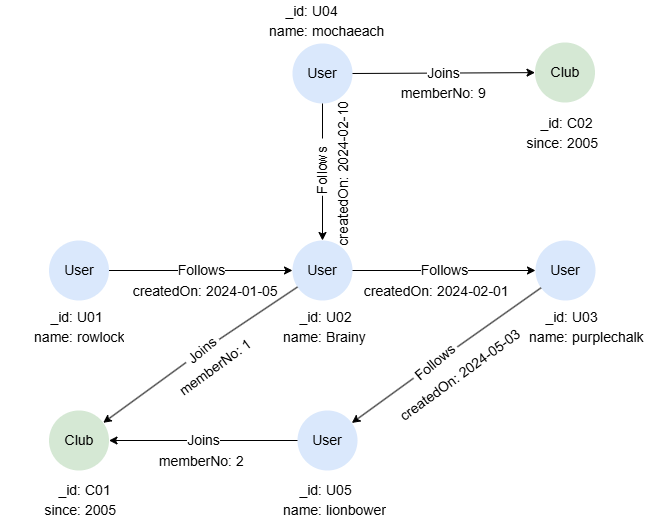
CREATE GRAPH myGraph {
NODE User ({name string}),
NODE Club ({since uint32}),
EDGE Follows ()-[{createdOn date}]->(),
EDGE Joins ()-[{memberNo uint32}]->()
} PARTITION BY HASH(Crc32) SHARDS [1]
INSERT (rowlock:User {_id: 'U01', name: 'rowlock'}),
(brainy:User {_id: 'U02', name: 'Brainy'}),
(purplechalk:User {_id: 'U03', name: 'purplechalk'}),
(mochaeach:User {_id: 'U04', name: 'mochaeach'}),
(lionbower:User {_id: 'U05', name: 'lionbower'}),
(c01:Club {_id: 'C01', since: 2005}),
(c02:Club {_id: 'C02', since: 2005}),
(rowlock)-[:Follows {createdOn: '2024-01-05'}]->(brainy),
(mochaeach)-[:Follows {createdOn: '2024-02-10'}]->(brainy),
(brainy)-[:Follows {createdOn: '2024-02-01'}]->(purplechalk),
(lionbower)-[:Follows {createdOn: '2024-05-03'}]->(purplechalk),
(brainy)-[:Joins {memberNo: 1}]->(c01),
(lionbower)-[:Joins {memberNo: 2}]->(c01),
(mochaeach)-[:Joins {memberNo: 9}]->(c02)
Simple Filtering
MATCH (c:Club)
FILTER c._id = "C01"
RETURN c
Result: c
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| C01 | Sys-gen | Club | {since: 2005} |
FOR item IN [1,2,3]
FILTER item > 1
RETURN item
Result: item
| item |
|---|
| 2 |
| 3 |
Filtering with Cartesian Product
This query returns users who follow Brainy and are also members of C02:
MATCH (u1:User)-[:Follows]->(:User {name: "Brainy"})
MATCH (u2:User)-({_id: "C02"})
FILTER u1 = u2
RETURN u1
Result: u1
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| U04 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "mochaeach"} |
Note that the Cartesian product is formed between u1 and u2, as they are produced by different MATCH statements, before the FILTER statement is applied to perform the filtering.

