Overview
The ORDER BY statement allows you to sort the intermediate result or output table based on the specified columns.
<order by statement> ::=
"ORDER BY" <sort specification> [ { "," <sort specification> }... ]
<sort specification> ::=
<value expression> [ "ASC" | "DESC" ] [ "NULLS FIRST" | "NULLS LAST" ]
Details
ASC(ascending) is applied by default. To reverse the order, you can explicitly use theDESC(descending) keyword.NULLS FIRSTandNULLS LASTcan be used to control whethernullvalues appear before or after non-null values. When null ordering is not explicitly specified:NULLS LASTis applied by default when ordering in theASCorder.NULLS FIRSTis applied by default when ordering in theDESCorder.
Example Graph

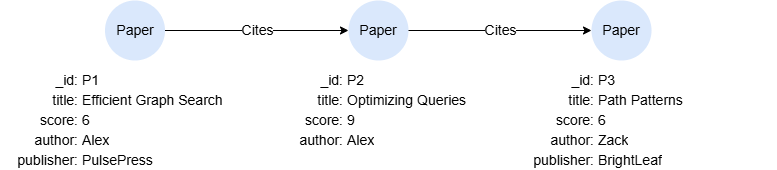
CREATE GRAPH myGraph {
NODE Paper ({title string, score uint32, author string, publisher string}),
EDGE Cites ()-[{weight uint32}]->()
} PARTITION BY HASH(Crc32) SHARDS [1]
INSERT (p1:Paper {_id:'P1', title:'Efficient Graph Search', score:6, author:'Alex', publisher:'PulsePress'}),
(p2:Paper {_id:'P2', title:'Optimizing Queries', score:9, author:'Alex'}),
(p3:Paper {_id:'P3', title:'Path Patterns', score:7, author:'Zack', publisher:'BrightLeaf'}),
(p1)-[:Cites {weight:2}]->(p2),
(p2)-[:Cites {weight:1}]->(p3)
Ordering by Property
MATCH (n:Paper)
ORDER BY n.score
RETURN n.title, n.score
Result:
| n.title | n.score |
|---|---|
| Efficient Graph Search | 6 |
| Path Patterns | 7 |
| Optimizing Queries | 9 |
Ordering by Node or Edge Variable
When a node or edge variable is specified, it is sorted on the _uuid of the nodes or edges.
MATCH (n:Paper)
RETURN n.title, element_id(n) ORDER BY n
Result:
| n.title | element_id(n) |
|---|---|
| Optimizing Queries | 8718971077612535810 |
| Efficient Graph Search | 8791028671650463745 |
| Path Patterns | 12033620403357220867 |
Ordering by Expression
MATCH p = (:Paper)->{1,2}(:Paper)
RETURN p, path_length(p) AS length ORDER BY length DESC
Result:
| p | length |
|---|---|
 |
2 |
 |
1 |
 |
1 |
Multi-level Ordering
When there are multiple specifications, it is sorted by the first specification listed, and for equals values, go to the next specification, and so on.
MATCH (n:Paper)
RETURN n.title, n.author, n.score
ORDER BY n.author DESC, n.score
Result:
| n.title | n.author | n.score |
|---|---|---|
| Path Patterns | Zack | 7 |
| Efficient Graph Search | Alex | 6 |
| Optimizing Queries | Alex | 9 |
Discarding and Retaining Records After Ordering
You may use the SKIP or LIMIT statement after the ORDER BY statement to skip a specified number of records from the top, or to limit the number of records retained.
To return titles of the two papers with the second and third highest scores:
MATCH (n:Paper)
RETURN n.title, n.score
ORDER BY n.score DESC SKIP 1 LIMIT 2
Result:
| n.title | n.score |
|---|---|
| Path Patterns | 7 |
| Efficient Graph Search | 6 |
Null Ordering
To return titles of the two papers with the second and third highest scores, ensuring null values appear at the front if applicable:
MATCH (n:Paper)
RETURN n.title, n.publisher
ORDER BY n.publisher NULLS FIRST
Result:
| n.title | n.score |
|---|---|
| Optimizing Queries | null |
| Path Patterns | BrightLeaf |
| Efficient Graph Search | PulsePress |

