Overview
The RETURN statement allows you to specify items to include in the query result. Each item is defined by an expression that can include variables, properties, functions, constants, etc.
<return statement> ::=
"RETURN" [ "DISTINCT" | "ALL" ] { <"*"> | <return items> } [ <group by clause> ]
<return items> ::=
<return item> [ { "," <return item> }... ]
<return item> ::=
<value expression> [ "AS" <identifier> ]
<group by clause> ::=
"GROUP BY" <grouping key> [ { "," <grouping key> }... ]
Details
- The asterisk
*returns all columns in the intermediate result table. See Returning All. - The keyword
AScan be used to rename a return item. See Return Item Alias. - The
RETURNstatement supports theGROUP BYclause. See Returning with Grouping. - The
DISTINCToperator can be used to deduplicate records. If neitherDISTINCTnorALLis specified,ALLis implicitly applied. See Returning Distinct Records.
Example Graph
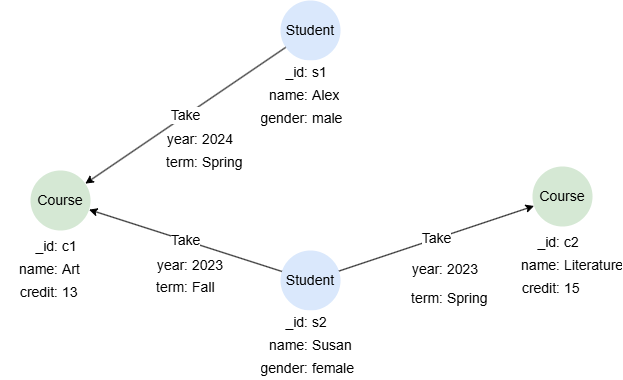
CREATE GRAPH myGraph {
NODE Student ({name string, gender string}),
NODE Course ({name string, credit uint32}),
EDGE Take ()-[{year uint32, term string}]->()
} PARTITION BY HASH(Crc32) SHARDS [1]
INSERT (alex:Student {_id: 's1', name: 'Alex', gender: 'male'}),
(susan:Student {_id: 's2', name: 'Susan', gender: 'female'}),
(art:Course {_id: 'c1', name: 'Art', credit: 13}),
(literature:Course {_id: 'c2', name: 'Literature', credit: 15}),
(alex)-[:Take {year: 2024, term: 'Spring'}]->(art),
(susan)-[:Take {year: 2023, term: 'Fall'}]->(art),
(susan)-[:Take {year: 2023, term: 'Spring'}]->(literature)
Returning Nodes
A variable bound to nodes returns all information about each node.
MATCH (n:Course)
RETURN n
Result: n
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| c1 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Art", credit: 13} |
| c2 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Literature", credit: 15} |
Returning Edges
A variable bound to edges returns all information about each edge.
MATCH ()-[e]->()
RETURN e
Result: e
_uuid |
_from |
_to |
_from_uuid |
_to_uuid |
schema |
values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sys-gen | s2 | c1 | UUID of s2 | UUID of c1 | Take | {year: 2023, term: "Fall"} |
| Sys-gen | s2 | c2 | UUID of s2 | UUID of c2 | Take | {year: 2023, term: "Spring"} |
| Sys-gen | s1 | c1 | UUID of s1 | UUID of c1 | Take | {year: 2024, term: "Spring"} |
Returning Paths
A variable bound to paths returns all information about the nodes and edges included in each path.
MATCH p = ()-[:Take {term: "Spring"}]->()
RETURN p
Result: p

Returning Labels
The function labels() can be used to return the labels of nodes and edges.
MATCH ({_id: "s2"})-[e]->(n)
RETURN labels(e), labels(n)
Result:
| labels(e) | labels(n) |
|---|---|
| Take | Course |
| Take | Course |
Returning Properties
The period operator . can be used to extract the value of a specified property from a variable bound to nodes or edges. The null value will be returned if the specified property is not found on the nodes or edges.
MATCH (:Student {name:"Susan"})-[]->(c:Course)
RETURN c.name, c.credit, c.type
Result:
| c.name | c.credit | c.type |
|---|---|---|
| Literature | 15 | null |
| Art | 13 | null |
Returning All
The asterisk * returns all columns in the intermediate result table. Note that the RETURN statement cannot include the GROUP BY clause when using *.
MATCH (s:Student {name:"Susan"})-[]->(c:Course)
RETURN *
Result:
s
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| s2 | Sys-gen | Student | {name: "Susan", gender: "female"} |
| s2 | Sys-gen | Student | {name: "Susan", gender: "female"} |
c
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| c1 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Art", credit: 13} |
| c2 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Literature", credit: 15} |
Return Item Alias
The AS keyword allows you to assign an alias to a return item.
MATCH (s:Student)-[t:Take]->(c:Course)
RETURN s.name AS Student, c.name AS Course, t.year AS TakenIn
Result:
| Student | Course | TakenIn |
|---|---|---|
| Alex | Art | 2024 |
| Susan | Art | 2023 |
| Susan | Literature | 2023 |
Returning with Aggregation
Aggregation functions, such as sum() and max(), can be directly applied in the RETURN statement.
MATCH (:Student {name:"Susan"})-[]->(c:Course)
RETURN sum(c.credit)
Result:
| sum(c.credit) |
|---|
| 28 |
Due to the use of the aggregate function, the c returned by this query contains only one record, as expected:
MATCH (:Student {name:"Susan"})-[]->(c:Course)
RETURN c, sum(c.credit)
Result:
c
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| c1 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Art", credit: 13} |
sum(c.credit)
| sum(c.credit) |
|---|
| 28 |
Returning by CASE
MATCH (n:Course)
RETURN n.name, CASE WHEN n.credit > 14 THEN "Y" ELSE "N" END AS Recommended
Result:
| n.name | Recommended |
|---|---|
| Art | N |
| Literature | Y |
Returning Limited Records
The LIMIT statement can be used to restrict the number of records retained for each return item.
MATCH (n:Course)
RETURN n.name LIMIT 1
Result:
| n.name |
|---|
| Art |
Returning Ordered Records
The ORDER BY statement can be used to sort the records.
MATCH (n:Course)
RETURN n ORDER BY n.credit DESC
Result: n
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| c2 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Literature", credit: 15} |
| c1 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Art", credit: 13} |
Returning with Grouping
The GROUP BY clause allows you to specify the keys to group the query result. After grouping, each group will keep only one record.
Grouping by One Key
MATCH ()-[e:Take]->()
RETURN e.term GROUP BY e.term
Result:
| e.term |
|---|
| Spring |
| Fall |
In the GQL standard, the grouping key must be a direct variable reference, where this query must be written as RETURN e.term AS <varName> GROUP BY <varName>. Ultipa simplifies this by allowing direct grouping on expressions, removing the need to introduce intermediate variables.
Grouping by Multiple Keys
MATCH ()<-[e:Take]-()
RETURN e.year, e.term GROUP BY e.year, e.term
Result:
| e.year | e.term |
|---|---|
| 2023 | Spring |
| 2024 | Spring |
| 2023 | Fall |
Grouping and Aggregation
When grouping is applied, any aggregation operation in the RETURN statement is performed on each group.
This query counts the number of Take edges for each Term:
MATCH ()-[e:Take]->()
RETURN e.term, count(e) GROUP BY e.term
Result:
| e.term | count(e) |
|---|---|
| Spring | 2 |
| Fall | 1 |
Returning Distinct Records
The DISTINCT operator deduplicates records for all return items. When DISTINCT is specified, each return item is implicly an operand of a grouping operation.
MATCH ()-[e]->()
RETURN DISTINCT e.year
This is equivalent to:
MATCH ()-[e]->()
RETURN e.year GROUP BY e.year
Result:
| e.year |
|---|
| 2023 |
| 2024 |
MATCH ()-[e]->()
RETURN DISTINCT e.year, e.term
This is equivalent to:
MATCH ()-[e]->()
RETURN e.year, e.term GROUP BY e.year, e.term
Result:
| e.year | e.term |
|---|---|
| 2023 | Fall |
| 2023 | Spring |
| 2024 | Spring |

