GQL supports various values and types to represent data within the graph database. Understanding these values and types is essential for effective query construction and data manipulation.
Property Value Types
A property value type refers to the data type of the values of a property. Ultipa supports the following property value types:
Numeric
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
INT/INTEGER/INT32/INTEGER32 |
32-bit signed integer ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. |
UINT/UINT32 |
32-bit unsigned integer ranging from 0 to 4,294,967,295. |
INT64/INTEGER64 |
64-bit signed integer ranging from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. |
UINT64 |
64-bit unsigned integer ranging from 0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615. |
FLOAT |
32-bit single-precision floating-point number supporting up to 6 digits after the decimal point. |
DOUBLE |
64-bit double-precision floating-point number supporting up to 15 significant digits. This includes all non-zero digits and any zeros between them, e.g., 0.0123456789012345. |
DECIMAL |
A fixed-point number with a specified precision (1 to 65, total number of digits) and scale (0 to 30, number of digits after the decimal point). E.g., DECIMAL(10,4) represents a number with up to 10 total digits, of which up to 4 can appear after the decimal point. |
Textual
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
STRING |
A sequence of characters enclosed in quotes, with a maximum size of 60,000 bytes. This is the default type when creating a property. |
TEXT |
A sequence of characters enclosed in quotes with no length limit. |
Temporal Instant
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
DATE |
A date value without any timezone information. E.g., 2025-01-01, 20250101. |
LOCAL DATETIME |
A date-time value without any timezone information. E.g., 2025-01-01 12:20:02, 20250101T122002.55254. |
LOCAL TIME |
A time value without any timezone information. E.g., 12:20:02, 122002.55254. |
ZONED DATETIME |
An instant date-time value that includes timezone information. E.g., 2025-01-01 12:20:02-1030, 20250101T122002.55254+0900. |
ZONED TIME |
A time value that includes timezone information. E.g., 12:20:02-1030, 122002.55254+0900. |
TIMESTAMP |
A Unix timestamp representing the number of seconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC. E.g., 1751422921 corresponds to 2025-07-02 02:22:01 UTC.When a date-time formatted value is provided, the system automatically converts it to a timestamp based on the local timezone, client settings, or SDK configuration. Likewise, when displaying a timestamp in date-time format, the output is adjusted according to the configured timezone. |
DATETIME |
A date-time value without timezone information, ranging from 1000-01-01 00:00:00.000000 to 9999-12-31 23:59:59.499999. This is an extended property type provided by Ultipa, similar to the standard GQL type LOCAL DATETIME, but with more flexible input formats. For example:
|
Date
- Format:
yyyy-[m]m-[d]doryyyymmdd - Range:
-9999-12-31to9999-12-31
Time
- Format:
hh:mm:ss[.fraction]orhhmmss[.fraction] - Range:
00:00:00.000000000to23:59:59.999999999
Date and Time
- Format: The date and time parts are joined by either a space or the letter
T. - Range:
-9999-01-01 00:00:00.000000000to9999-12-31 23:59:59.999999999
Timezone
- Format: Represented as a UTC offset in the form of
±hh:mmor±hhmm, appended directly to the time value. - Range:
UTC-15:00toUTC+15:00
Temporal Duration
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
DURATION(YEAR TO MONTH) |
A time duration measured in years and months only. E.g., P2Y5M (2 years and 5 months), -P1Y2M (minus 1 year and 2 months).
|
DURATION(DAY TO SECOND) |
A time duration measured in days, hours, minutes, seconds, and optional fractional seconds. E.g., P3DT4H (3 days and 4 hours), -P1DT2H3M4.12S (minus 1 day, 2 hours, 3 minutes, and 4.12 seconds).
|
Boolean
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
BOOL |
Represents two possible values:
|
Spatial
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
POINT |
A two-dimensional geographical coordinate (latitude, longitude) that indicate a specific position. The coordinate values are stored as DOUBLE. |
POINT3D |
A three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate (x, y, z) that indicate a specific position. The coordinate values are stored as DOUBLE. |
Record
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
RECORD |
A set of fields, each such field has a name and a value. |
Binary
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
BLOB |
Stores binary data, which can be used for images, audio, video, or other unstructured files. |
List
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
LIST<subType> |
An ordered collection of elements of the specified subtype. Supports all of the above types as subtypes, except for BOOL. |
Constructed Value Types
A constructed value type is a data type comprising composite elements. GQL defines the following constructed value types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
PATH |
Represents the path value type. A path value encapsulates the ordered list of nodes and edges that form a path in the graph. |
LIST or ARRAY |
Represents the list value type. A list value is an ordered collection of elements of the same or different types. A list value is either a regular list value or a group list value. A regular list value is a list value that is not a group list value. |
RECORD |
Represents the record type. A record is a set of fields, each such field has a name and a value. |
Result Types
A result type refers to the data type of the values returned by a query. Ultipa defines the following result types.
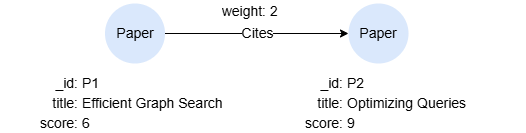
RESULT_TYPE_NODE
This query returns all nodes labeled Paper bound to the variable n:
MATCH (n:Paper) RETURN n
Data structure of n:
{
"data": [
{
"id": "P2",
"uuid": "8718971077612535835",
"schema": "Paper",
"values": {
"title": "Optimizing Queries",
"score": 9
}
},
{
"id": "P1",
"uuid": "8791028671650463770",
"schema": "Paper",
"values": {
"title": "Efficient Graph Search",
"score": 6
}
}
],
"alias": "n",
"type": 2,
"type_desc": "RESULT_TYPE_NODE"
}
RESULT_TYPE_EDGE
This query returns all outgoing edges labeled Cites bound to the variable e:
MATCH ()-[e:Cites]->() RETURN e
Data structure of e:
{
"data": [
{
"from": "P1",
"to": "P2",
"uuid": "1",
"from_uuid": "8791028671650463770",
"to_uuid": "8718971077612535835",
"schema": "Cites",
"values": {
"weight": 2
}
}
],
"alias": "e",
"type": 3,
"type_desc": "RESULT_TYPE_EDGE"
}
RESULT_TYPE_PATH
This query returns all outgoing 1-step paths bound to the variable p:
MATCH p = ()-[]->() RETURN p
Data structure of p:
{
"data": [
{
"nodes": [
{
"id": "P1",
"uuid": "8791028671650463770",
"schema": "Paper",
"values": {
"title": "Efficient Graph Search",
"score": 6
}
},
{
"id": "P2",
"uuid": "8718971077612535835",
"schema": "Paper",
"values": {
"title": "Optimizing Queries",
"score": 9
}
}
],
"edges": [
{
"from": "P1",
"to": "P2",
"uuid": "1",
"from_uuid": "8791028671650463770",
"to_uuid": "8718971077612535835",
"schema": "Cites",
"values": {
"weight": 2
}
}
],
"length": 1
}
],
"alias": "p",
"type": 1,
"type_desc": "RESULT_TYPE_PATH"
}
RESULT_TYPE_ATTR
This query returns the title property of nodes labeled Paper:
MATCH (n:Paper) RETURN n.title
Data structure of n.title:
{
"data": {
"alias": "n.title",
"type": 4,
"type_desc": "RESULT_TYPE_ATTR",
"values": [
"Optimizing Queries",
"Efficient Graph Search"
]
},
"alias": "n.title",
"type": 4,
"type_desc": "RESULT_TYPE_ATTR"
}
RESULT_TYPE_TABLE
This query returns a table bound to the variable table:
MATCH (n:Paper) RETURN table(n.title, n.score) AS table
Data structure of table:
{
"data": {
"name": "table",
"alias": "table",
"headers": [
"n.title",
"n.score"
],
"rows": [
[
"Optimizing Queries",
"9"
],
[
"Efficient Graph Search",
"6"
]
]
},
"alias": "table",
"type": 5,
"type_desc": "RESULT_TYPE_TABLE"
}
Null Value
The null value is a special value available in all nullable types. Any non-null value is a material value.
Null Scenarios
The null values can arise in various contexts, including:
- Default Assignment: When nodes or edges are inserted, nullable properties that lack specified values automatically receive
null. - Explicit Null Specification: During node or edge insertion, nullable properties can be intentionally set to
null. - Value Removal: Removing a property’s value sets it to
null. - New Property Assignment: When adding a new property to a label, any existing nodes or edges with that label are assigned
nullfor the new property by default. - Nonexistent Property References: Referencing a property that does not exist returns
null. - Optional Matching: When the
OPTIONALkeyword is used with theMATCHstatement, if no result is found for the pattern,MATCHyieldsnullinstead of empty return. - NULLIF Expression: The
NULLIFexpression returnsnullif the two compared values are equal.
Null in Comparisons
The null value is not comparable to any other value due to its inherently unknown nature. Consequently, comparisons involving null using normal operators such as = or <> do not typically yield true or false but rather an unknown result, also represented by null.
| Example | Result |
|---|---|
RETURN null = null |
null |
RETURN null > 3 |
null |
RETURN [1,null,2] <> [1,null,2] |
null |
RETURN 3 IN [1,null,2] |
null |
RETURN null IN [1,2] |
null |
RETURN null IN [] |
0 |
Comparisons involving null require special handling with null predicates (IS NULL and IS NOT NULL).
| Example | Result |
|---|---|
RETURN null IS NULL |
1 |
RETURN null IS NOT NULL |
0 |
Null Treatments
The null values receive special treatment in some contexts. For instance:
- Aggregate functions typically ignore
nullvalues. - The
GROUP BYclause groups allnullvalues together. - The
ORDER BYstatement allows for null ordering using theNULLS FIRSTandNULL LASTkeywords.

