A graph database is a type of database that stores, queries, and manages data in the form of graphs, instead of tables or documents. This approach enables users to organize data in a natural representation of relationships that aligns with how humans naturally think, making querying and analyzing highly connected data much easier and more efficient.
What is a Graph
An instance of the Ultipa graph database can host one or more graphs, each representing a unique dataset or domain of interconnected nodes and edges.
Graph Elements
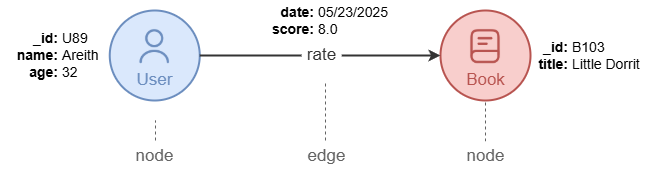
A graph consists of the following two elements:
- Nodes (or vertices), which represent entities (e.g.,
User,Book,Country). - Edges, which represent relationships between entities (e.g.,
rate,purchased,locate_in).
Nodes are uniquely identified by the system property _id (string type). Edges connect a source node to a destination node and store connected nodes' _id in the system properties _from and _to.
Graph Structure
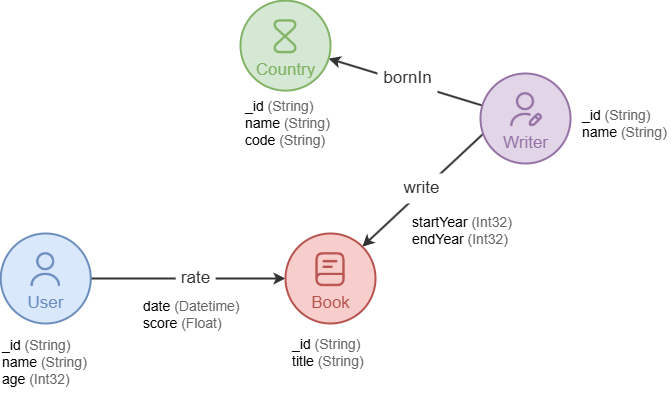
Before creating a graph, it is essential to design an appropriate graph structure (or model) based on the specific scenario.
A graph structure is defined by:
- Types (or Labels, Schemas), which refer to specific types for nodes and edges. Each node or edge is assigned with exactly one type. For example, a
Usernode, arateedge. - Properties, which are the attributes associated with node and edge types. Each property has a specific value type. For example, a
Usernode might have properties likename(stringtype) andage(int32type).
The graph structure can evolve over time and is subject to flexible changes.
Paths
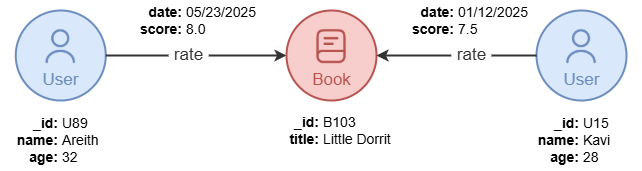
A path in a graph represents a sequential traversal of connected graph elements. A path always:
- starts and ends with a node, and
- alternates between nodes and edges.
A path may comprise a single node.
In Ultipa, a path allows nodes to be revisited but not edges by default.
How Graph Databases Work
In a graph database, data is represented using nodes and edges. Traversing is the process of navigating through the graph by moving from one node to another via connected edges. This is conceptually similar to the JOINs in relational databases to link related data. However, graph database traversal is far more efficient, because relationships are inherently stored within the graph. This makes graph databases exceptionally well-suited for scenarios demanding rapid exploration of interconnected data, easily handling paths of 5, 10, 20, or even more hops with remarkable speed.
When to Use Graph Databases
Graph database is a versatile, general-purpose database designed to model wild range of real-life scenarios, including but not limited to, financial systems, supply chain management, and social networks. It demonstrates exceptional utility in environments characterized by highly connected data, where the interrelationships between data points are as critical as the data itself.
By inherently storing and managing these relationships, graph databases circumvent the need for the often complex and costly join operations typically found in relational databases, thereby delivering significantly enhanced performance. Furthermore, their advanced querying capabilities simplify the process of expressing and analyzing intricate patterns and connections within data.

