Graph Query Language (GQL) is the ISO/IEC-standardized query language for graph databases, similar to how SQL is used with relational databases. The first version of the GQL standard was officially published in April 2024, making it the first new standardized database language since SQL was introduced in 1987.
This page covers the basics of GQL. For the complete guide, refer to GQL.
GQL Key Syntax
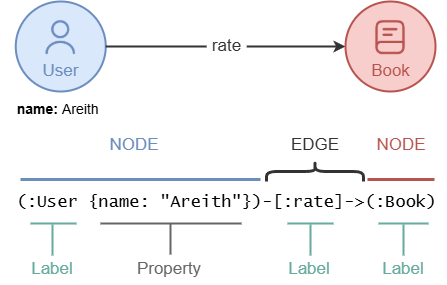
Node Patterns
A node pattern is used to match nodes in a graph. It is written using a pair of parentheses (), where you can specify the node's label and properties.
To match any node:
()
To match User nodes:
(:User)
To match User nodes whose name is Areith and age is 32:
(:User {name: "Areith", age: 32})
To match nodes whose name is Areith:
({name: "Areith"})
Edge Patterns
An edge pattern is used to match edges in a graph. It is written using a pair of square brackets [], where you can specify the edge's label and properties. You may also indicate the direction of the edge in the pattern.
To match any edge:
-[]-
To match rate edges pointing to the right:
-[:rate]->
To match rate edges pointing to the left with a score of 8:
<-[:rate {score: 8}]-
Path Patterns
A path pattern is used to match paths in a graph. It consists of a sequence of node and edge patterns. Every path pattern must:
- Begin and end with a node pattern
- Alternate strictly between node and edge patterns
To match paths that start from Areith, follow outgoing rate edges and end at Book nodes:
(:User {name: "Areith"})-[:rate]->(:Book)
To match paths describing the common connection between Areith and Kavi to any Book node:
(:User {name: "Areith"})-[]-(:Book)-[]-(:User {name: "Kavi"})
Label Expression
A label expression specifies the type or label of a node or edge in a pattern. It is denoted by a colon : prefix. For example, (:Book) matches any node with the label Book.
Property Specification
Property key-value pairs can be enclosed in a pair of curly braces {} inside a node or edge pattern. This allows applying joint equalities to filter nodes or edges based on the values of their properties.
Variables
A variable is an identifier used to represent data retrieved from the database or manually defined, allowing it to be referenced throughout the query.
To assign a variable p to represent the whole paths:
p = (:User {name: "Areith"})-[:rate]->(:Book)
To assign a variable books to represent the books that Areith once rated:
(:User {name: "Areith"})-[:rate]->(books:Book)
To assign a variable r to represent the rate edges connected to Areith, and use a WHERE clause to filter rate edges with a score greater than 8:
(:User {name: "Areith"})-[r:rate WHERE r.score > 8]-(:Book)
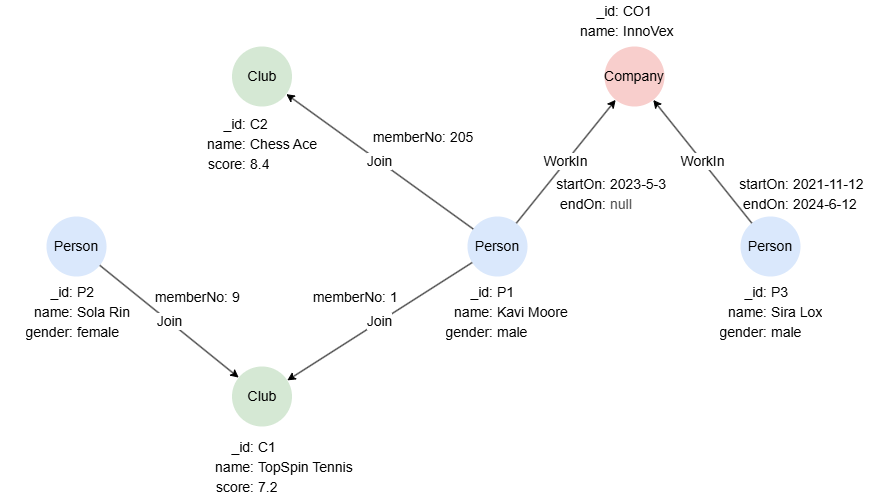
Example Graph
The following examples run against this graph:
Reading from the Database
You can read nodes, edges, and paths from a graph. To retrieve them, write the appropriate pattern in a MATCH statement and use the RETURN clause to specify the output.
Nodes
This query retrieves Person nodes whose gender is male:
MATCH (p:Person {gender: "male"})
RETURN p
Result: p
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Sys-gen | Person | {name: "Kavi Moore", gender: "male"} |
| P2 | Sys-gen | Person | {name: "Sira Lox", gender: "male"} |
Edges
This query retrieves WorkIn edges whose endOn is null:
MATCH -[e:WorkIn WHERE e.endOn IS NULL]->
RETURN e
Result: e
_uuid |
_from |
_to |
_from_uuid |
_to_uuid |
schema |
values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sys-gen | P1 | CO1 | UUID of P1 | UUID of CO1 | WorkIn | {StartOn: "2023-05-03 00:00:00", endOn: null} |
Paths
This query retrieves all paths showing that a person currently works at the company InnoVex, and returns both the paths and the person's name:
MATCH p = (n:Person)-[e:WorkIn WHERE e.endOn IS NULL]->(:Company {name: "InnoVex"})
RETURN p, n.name
Result:
| p | n.name |
|---|---|
| (:Person {_id: "P1", name: "Kavi Moore", gender: "male"})-[:WorksIn {startOn: "2023-05-03 00:00:00", endOn: null}]->(:Company {_id: "C01", name: "InnoVex"}) | Kavi Moore |
Writing to the Database
You can write to the database by inserting, updating and deleting nodes and edges.
Insertion
The INSERT statement serves the purpose of creating new nodes and edges in the database.
This query inserts a Person node, its _id is set to P4, and name to Tiva Jorn:
INSERT (:Person {_id: "P4", name: "Tiva Jorn"})
This query inserts an WorkIn edge pointing from node P4 to the node CO1, its startOn is set to 2025-3-1:
MATCH (innovex {_id: "CO1"}), (tiva {_id: "P4"})
INSERT (tiva)-[:WorkIn {startOn: "2025-3-1"}]->(innovex)
Updating
The SET statement serves the purpose of updating the properties of existing nodes and edges in the database. The nodes or edges to be updated must firstly be retrieved from the database using the MATCH statement.
This query updates the node P4 by setting its gender to female:
MATCH (tiva {_id: "P4"})
SET tiva.gender = "female"
This query updates the WorkIn edge pointing from node P4 to the node CO1 by setting its startOn to 2025-4-1:
MATCH ({_id: "P4"})-[e:WorkIn]->({_id: "CO1"})
SET e.startOn = "2025-4-1"
Deletion
The DELETE statement serves the purpose of deleting nodes and edges in the database. The nodes or edges to be deleted must firstly be retrieved from the database using the MATCH statement. By default, you cannot delete a node who still has edges attached to it.
This query deletes the WorkIn edge pointing from node P4 to node CO1:
MATCH ({_id: "P4"})-[e:WorkIn]->({_id: "CO1"})
DELETE e
This query deletes the node P4:
MATCH (n {_id: "P4"})
DELETE n

