Overview
The Bipartite algorithm is used to determine whether a given graph is a bipartite graph. The algorithm identifies and leverages the structure of bipartite graphs to enable efficient resource allocation, task assignment, and group optimization in various scenarios.
The Bipartite algorithm returns 1 if the graph is bipartite; otherwise, it returns 0.
Concepts
Bipartite Graph
A bipartite graph, also known as a bigragh, is a graph in which the nodes can be divided into two disjoint sets such that every edge connects a node from one set to a node in the other. In other words, no edge connects nodes within the same set.
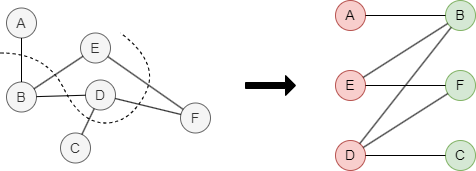
This example graph is bipartite. The nodes can be partitioned into sets V1 = {A, D, E} and V2 = {B, C, F}.
Coloring Method
To determine if a graph is bipartite, one common approach is to perform a graph traversal and assign each visited node to one of two different sets. This process is often referred to as "coloring" the nodes. During traversal, if an edge is found that connects two nodes within the same set, the graph is not bipartite. Conversely, if all edges connect nodes from different sets, the graph is bipartite.
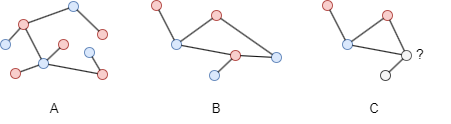
In this example, both graph A and graph B are bipartite. Graph C is not bipartite as it contains an odd cycle. An odd cycle is a cycle that has an odd number of nodes. Bipartite graphs cannot contain odd cycles, as it is impossible to color all nodes in an odd cycle using only two colors while satisfying the bipartite condition. This property, where bipartite graphs never contain any odd cycles, is a fundamental characteristic of bipartite graphs.
Considerations
- A self-loop connects a node to itself, meaning both endpoints are the same node. Therefore, any graph containing a self-loop is not bipartite.
- The Bipartite algorithm ignores the direction of edges but calculates them as undirected edges.
Example Graph
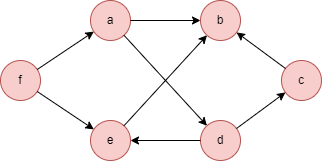
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
INSERT (a:default {_id: "a"}),
(b:default {_id: "b"}),
(c:default {_id: "c"}),
(d:default {_id: "d"}),
(e:default {_id: "e"}),
(f:default {_id: "f"}),
(a)-[:default]->(b),
(a)-[:default]->(d),
(c)-[:default]->(b),
(d)-[:default]->(c),
(d)-[:default]->(e),
(e)-[:default]->(b),
(f)-[:default]->(a),
(f)-[:default]->(e);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"a"}, {_id:"b"}, {_id:"c"}, {_id:"d"}, {_id:"e"}, {_id:"f"}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"a", _to:"b"}, {_from:"a", _to:"d"}, {_from:"c", _to:"b"}, {_from:"d", _to:"c"}, {_from:"d", _to:"e"}, {_from:"e", _to:"b"}, {_from:"f", _to:"a"}, {_from:"f", _to:"e"}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: bipartite
The algorithm does not require any parameters.
File Writeback
CALL algo.bipartite.write("my_hdc_graph", {},
{
file: {
filename: "isBipartite"
}
})
algo(bipartite).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "isBipartite"
}
})
bipartite_result: 1
Stats Writeback
CALL algo.bipartite.write("my_hdc_graph", {},
{
stats: {}
})
exec{
algo(bipartite).params().stream() as result
return result
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| bipartite_result |
|---|
| true |
Full Return
CALL algo.bipartite.run("my_hdc_graph") YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(bipartite).params() as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| bipartite_result |
|---|
| 1 |
Stream Return
CALL algo.bipartite.stream("my_hdc_graph") YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(bipartite).params().stream() as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| bipartite_result |
|---|
| 1 |
Stats Return
CALL algo.bipartite.stats("my_hdc_graph") YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(bipartite).params().stats() as result
return result
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| bipartite_result |
|---|
| 1 |

