Overview
Conductance is a metric used to evaluate the quality of a community or cluster within a graph. Studies have shown that scoring functions that are based on conductance best capture the structure of ground-truth communities.
- J. Yang, J. Leskovec, Defining and Evaluating Network Communities based on Ground-truth (2012)
Concepts
Conductance
Intuitively, a good community should have strong internal connections and only weak connections to the rest of the graph.
For a community C and its complement C', the conductance of C is defined as the ratio of the cut size (the number of edges crossing between C and C') to the minimum volume of C and C' (i.e., the sum of degrees of nodes within each set):
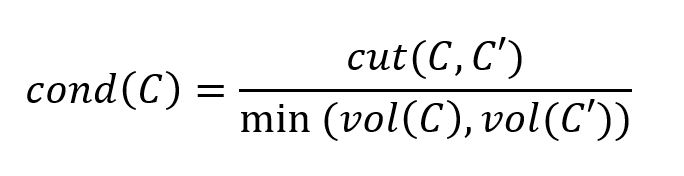
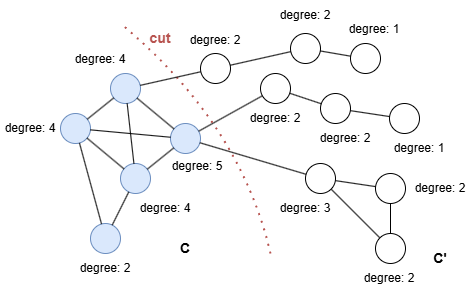
In the example below, the community C is connected to the rest of the graph with three edges, i.e., cut(C, C') = 3. The conductance of C is then cond(C) = 3/min(19, 17) = 3/17 = 0.176471.
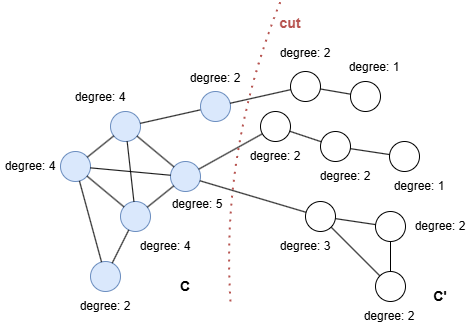
If we adjust the cut to inlcude one more node in C, the conductance becomes cond(C) = 3/min(21, 15) = 3/15 = 0.2.
A small conductance value is desirable in community detection because it indicates a dense community with relatively few edges connecting to the outside. Conversely, a large conductance value means the community is loosely connected internally and has many edges reaching nodes outside the community. This suggests that the community is not tightly knit.
Example Graph
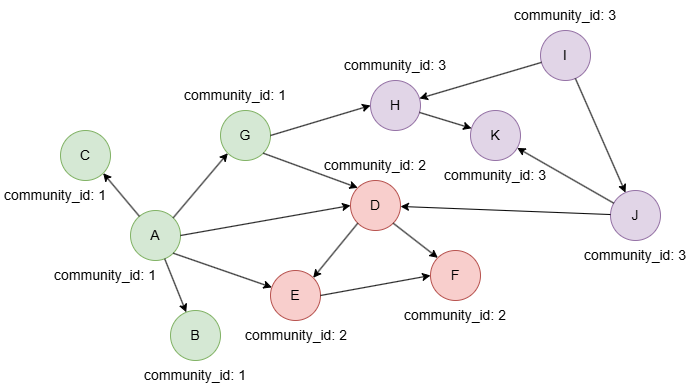
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
ALTER NODE default ADD PROPERTY {
community_id uint32
};
INSERT (A:default {_id: "A", community_id: 1}),
(B:default {_id: "B", community_id: 1}),
(C:default {_id: "C", community_id: 1}),
(D:default {_id: "D", community_id: 2}),
(E:default {_id: "E", community_id: 2}),
(F:default {_id: "F", community_id: 2}),
(G:default {_id: "G", community_id: 1}),
(H:default {_id: "H", community_id: 3}),
(I:default {_id: "I", community_id: 3}),
(J:default {_id: "J", community_id: 3}),
(K:default {_id: "K", community_id: 3}),
(A)-[:default]->(B),
(A)-[:default]->(C),
(A)-[:default]->(D),
(A)-[:default]->(E),
(A)-[:default]->(G),
(D)-[:default]->(E),
(D)-[:default]->(F),
(E)-[:default]->(F),
(G)-[:default]->(D),
(G)-[:default]->(H),
(H)-[:default]->(K),
(I)-[:default]->(H),
(I)-[:default]->(J),
(J)-[:default]->(D),
(J)-[:default]->(K);
create().node_property(@default, "community_id", uint32);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A", community_id: 1}, {_id:"B", community_id: 1}, {_id:"C", community_id: 1}, {_id:"D", community_id: 2}, {_id:"E", community_id: 2}, {_id:"F", community_id: 2}, {_id:"G", community_id: 1}, {_id:"H", community_id: 3}, {_id:"I", community_id: 3}, {_id:"J", community_id: 3}, {_id:"K", community_id: 3}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"A", _to:"B"}, {_from:"A", _to:"C"}, {_from:"A", _to:"D"}, {_from:"A", _to:"E"}, {_from:"A", _to:"G"}, {_from:"D", _to:"E"}, {_from:"D", _to:"F"}, {_from:"E", _to:"F"}, {_from:"G", _to:"D"}, {_from:"G", _to:"H"}, {_from:"J", _to:"D"}, {_from:"I", _to:"H"}, {_from:"I", _to:"J"}, {_from:"H", _to:"K"}, {_from:"J", _to:"K"}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: conductance
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
community_property |
"<@schema.?>property" |
/ | / | No | The numeric node property holds the values representing community IDs. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.conductance.write("my_hdc_graph", {
community_property: "community_id"
}, {
file: {
filename: "conductance"
}
})
algo(conductance).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
community_property: "community_id"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "conductance"
}
})
community,conductance
2,0.4
1,0.4
3,0.2
Full Return
CALL algo.conductance.run("my_hdc_graph", {
community_property: "community_id"
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(conductance).params({
community_property: "community_id"
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| community | conductance |
|---|---|
| 2 | 0.4 |
| 1 | 0.4 |
| 3 | 0.2 |
Stream Return
CALL algo.conductance.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
community_property: "community_id"
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(conductance).params({
community_property: "community_id"
}).stream() as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| community | conductance |
|---|---|
| 2 | 0.4 |
| 1 | 0.4 |
| 3 | 0.2 |

