Overview
The HANP (Hop Attenuation & Node Preference) algorithm extends the traditional Label Propagation algorithm (LPA) by incorporating a label score attenuation mechanism and accounting for the influence of neighbor node degree on neighbor label weight. The goal of HANP is to improve the accuracy and robustness of community detection in networks. It was proposed in 2009:
- I.X.Y. Leung, P. Hui, P. Liò, J. Crowcroft, Towards real-time community detection in large networks (2009)
Concepts
Hop Attenuation
HANP associates each label with a score which decreases as it propagates from its origin. Initially, all labels are assigned a score of 1. Each time a node adopts a new label from its neighborhood, the score of that label is attenuated by subtracting a hop attenuation factor δ (0 < δ < 1).
The hop attenuation mechanism helps limit the spread of labels to nearby nodes and prevents any single label from dominating the entire network.
Node Preference
In the calculation of the new maximal label, HANP incorporates node preference based on node degree. When node j ∈ Ni propagates its label L to node i, the weight of label L is calculated by:
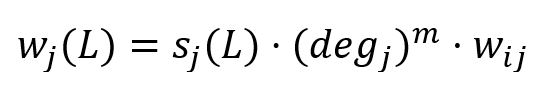
where,
- sj(L) is the score of label L in j.
- degj is the degree of j. When m > 0, more preference is given to node with high degree; m < 0, more preference is given to node with low degree; m = 0, no node preference is applied.
- wij is the sum of edge weights between i and j.
Given the edge weights and label scores shown in the example below, if we set m = 2 and δ = 0.2, the blue node will update its label from d to a. The score of label a in the blue node will be attenuated to 0.6.
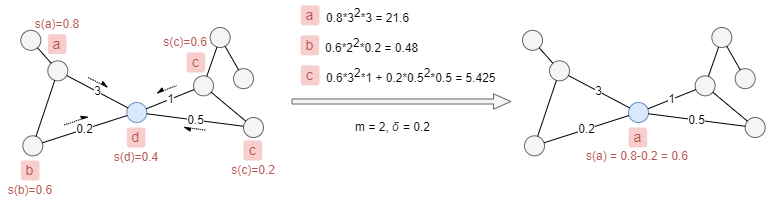
Considerations
- HANP treats all edges as undirected, ignoring their original direction.
- Node with self-loops propagates its current label(s) to itself, and each self-loop is counted twice.
- When the selected label is equal to the current label, let δ = 0.
- HANP follows the synchronous update principle, where all nodes update their labels simultaneously based on their neighbors' labels. The label score mechanism helps prevent label oscillations.
- Due to factors such as the order of nodes, the random selection among labels with equal weights and parallel computations, the community detection results of HANP may vary between runs.
Example Graph
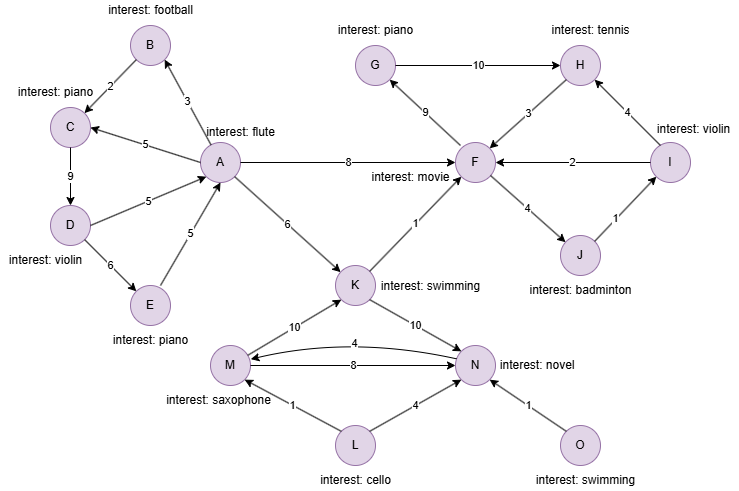
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
ALTER GRAPH CURRENT_GRAPH ADD NODE {
user ({interest string})
};
ALTER GRAPH CURRENT_GRAPH ADD EDGE {
connect ()-[{strength int32}]->()
};
INSERT (A:user {_id:"A",interest:"flute"}),
(B:user {_id:"B",interest:"football"}),
(C:user {_id:"C",interest:"piano"}),
(D:user {_id:"D",interest:"violin"}),
(E:user {_id:"E",interest:"piano"}),
(F:user {_id:"F",interest:"movie"}),
(G:user {_id:"G",interest:"piano"}),
(H:user {_id:"H",interest:"tennis"}),
(I:user {_id:"I",interest:"violin"}),
(J:user {_id:"J",interest:"badminton"}),
(K:user {_id:"K",interest:"swimming"}),
(L:user {_id:"L",interest:"cello"}),
(M:user {_id:"M",interest:"saxophone"}),
(N:user {_id:"N",interest:"novel"}),
(O:user {_id:"O",interest:"swimming"}),
(A)-[:connect {strength:3}]->(B),
(A)-[:connect {strength:5}]->(C),
(A)-[:connect {strength:8}]->(F),
(A)-[:connect {strength:6}]->(K),
(B)-[:connect {strength:2}]->(C),
(C)-[:connect {strength:9}]->(D),
(D)-[:connect {strength:5}]->(A),
(D)-[:connect {strength:6}]->(E),
(E)-[:connect {strength:5}]->(A),
(F)-[:connect {strength:9}]->(G),
(F)-[:connect {strength:4}]->(J),
(G)-[:connect {strength:10}]->(H),
(H)-[:connect {strength:3}]->(F),
(I)-[:connect {strength:2}]->(F),
(I)-[:connect {strength:4}]->(H),
(J)-[:connect {strength:1}]->(I),
(K)-[:connect {strength:1}]->(F),
(K)-[:connect {strength:10}]->(N),
(L)-[:connect {strength:1}]->(M),
(L)-[:connect {strength:4}]->(N),
(M)-[:connect {strength:10}]->(K),
(M)-[:connect {strength:8}]->(N),
(N)-[:connect {strength:4}]->(M),
(O)-[:connect {strength:1}]->(N);
create().node_schema("user").edge_schema("connect");
create().node_property(@user,"interest",string).edge_property(@connect,"strength",int32);
insert().into(@user).nodes([{_id:"A",interest:"flute"}, {_id:"B",interest:"football"}, {_id:"C",interest:"piano"}, {_id:"D",interest:"violin"}, {_id:"E",interest:"piano"}, {_id:"F",interest:"movie"}, {_id:"G",interest:"piano"}, {_id:"H",interest:"tennis"}, {_id:"I",interest:"violin"}, {_id:"J",interest:"badminton"}, {_id:"K",interest:"swimming"}, {_id:"L",interest:"cello"}, {_id:"M",interest:"saxophone"}, {_id:"N",interest:"novel"}, {_id:"O",interest:"swimming"}]);
insert().into(@connect).edges([{_from:"A",_to:"B",strength:3}, {_from:"A",_to:"C",strength:5}, {_from:"A",_to:"F",strength:8}, {_from:"A",_to:"K",strength:6}, {_from:"B",_to:"C",strength:2}, {_from:"C",_to:"D",strength:9}, {_from:"D",_to:"A",strength:5}, {_from:"D",_to:"E",strength:6}, {_from:"E",_to:"A",strength:5}, {_from:"F",_to:"G",strength:9}, {_from:"F",_to:"J",strength:4}, {_from:"G",_to:"H",strength:10}, {_from:"H",_to:"F",strength:3}, {_from:"I",_to:"H",strength:4}, {_from:"I",_to:"F",strength:2}, {_from:"J",_to:"I",strength:1}, {_from:"K",_to:"F",strength:1}, {_from:"K",_to:"N",strength:10}, {_from:"L",_to:"M",strength:1}, {_from:"L",_to:"N",strength:4}, {_from:"M",_to:"N",strength:8}, {_from:"M",_to:"K",strength:10}, {_from:"N",_to:"M",strength:4}, {_from:"O",_to:"N",strength:1}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: hanp
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
node_label_property |
"<@schema.?><property>" |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies numeric or string node property used to initialize node labels; nodes without the specified property are ignored. The system will generate the labels if it is unset. |
edge_weight_property |
"<@schema.?><property>" |
/ | / | Yes | Numeric edge property used as the edge weights. |
m |
Float | / | 0 |
Yes | The power exponent of the neighbor node degree:
|
delta |
Float | [0, 1] | 0 |
Yes | Hop attenuation δ. |
loop_num |
Integer | ≥1 | 5 |
Yes | Number of propagation iterations. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.hanp.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
loop_num: 10,
edge_weight_property: "strength",
m: 2,
delta: 0.2
}, {
file: {
filename: "hanp"
}
})
algo(hanp).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
return_id_uuid: "id",
loop_num: 10,
edge_weight_property: "strength",
m: 2,
delta: 0.2
}).write({
file: {
filename: "hanp"
}
})
DB Writeback
Writes each label_1 and its score_1 from the results to the specified node properties. The property types are string and float, respectively.
CALL algo.hanp.write("my_hdc_graph", {
node_label_property: "@user.interest",
m: 0.1,
delta: 0.3
}, {
db: {
property: "lab"
}
})
algo(hanp).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
node_label_property: "@user.interest",
m: 0.1,
delta: 0.3
}).write({
db: {
property: "lab"
}
})
The label and its score of each node is written to new properties lab_1 and score_1.
Stats Writeback
CALL algo.hanp.write("my_hdc_graph", {
node_label_property: "@user.interest",
m: 0.1,
delta: 0.3
}, {
stats: {}
})
algo(hanp).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
node_label_property: "@user.interest",
m: 0.1,
delta: 0.3
}).write({
stats: {}
})
Full Return
CALL algo.hanp.run("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
loop_num: 12,
node_label_property: "@user.interest",
m: 1,
delta: 0.2
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(hanp).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
loop_num: 12,
node_label_property: "@user.interest",
m: 1,
delta: 0.2
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Stream Return
CALL algo.hanp.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
loop_num: 12,
node_label_property: "@user.interest",
m: 1,
delta: 0.2
}) YIELD r
RETURN r.label_1 AS label, count(r) GROUP BY label
exec{
algo(hanp).params({
loop_num: 12,
node_label_property: "@user.interest",
m: 1,
delta: 0.2
}).stream() as r
group by r.label_1 as label
return table(label, count(r))
} on my_hdc_graph
Stats Return
CALL algo.hanp.stats("my_hdc_graph", {
loop_num: 5,
node_label_property: "interest",
m: 0.6,
delta: 0.2
}) YIELD s
RETURN s
exec{
algo(hanp).params({
loop_num: 5,
node_label_property: "interest",
m: 0.6,
delta: 0.2
}).stats() as s
return s
} on my_hdc_graph

