Overview
The k-Core algorithm finds the largest connected subgraph where every node has at least degree k. It is commonly employed to identify tightly connected groups in a graph for further analysis. Common applications include financial risk control, social network analysis, and biological studies. The algorithm runs in linear time, making it efficient for large graphs. Its output is also easy to interpret, helping reveal structural patterns and relationships.
The widely accepted concept of k-core was first introduced by Seidman:
- S.B. Seidman, Network Structure And Minimum Degree. Soc Netw 5:269-287 (1983)
Concepts
k-Core
The k-core of a graph is computed through iterative pruning. Nodes with a degree less than k are successively removed until all remaining nodes have degrees greater than or equal to k.
Below is the pruning process to get the 3-core of the graph. In the first round, nodes {a, d, f} with degree less than 3 are removed , which then affects the removal of node b in the second round. After the second round, all remaining nodes have a degree of at least 3. Therefore, the pruning process ends, and the 3-core of this graph is induced by nodes {c, e, g, h}.
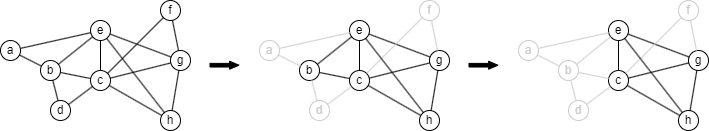
Ultipa's k-Core algorithm identifies the k-core in each connected component.
Considerations
- The k-Core algorithm ignores self-loops in the graph. They are not counted when calculating the degree of a node.
- The k-Core algorithm treats all edges as undirected, ignoring their original direction.
Example Graph
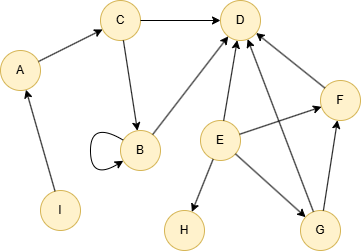
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
INSERT (A:default {_id: "A"}),
(B:default {_id: "B"}),
(C:default {_id: "C"}),
(D:default {_id: "D"}),
(E:default {_id: "E"}),
(F:default {_id: "F"}),
(G:default {_id: "G"}),
(H:default {_id: "H"}),
(I:default {_id: "I"}),
(A)-[:default]->(C),
(B)-[:default]->(B),
(B)-[:default]->(D),
(C)-[:default]->(B),
(C)-[:default]->(D),
(E)-[:default]->(D),
(E)-[:default]->(F),
(E)-[:default]->(G),
(E)-[:default]->(H),
(F)-[:default]->(D),
(G)-[:default]->(D),
(G)-[:default]->(F),
(I)-[:default]->(A);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"}, {_id:"B"}, {_id:"C"}, {_id:"D"}, {_id:"E"}, {_id:"F"}, {_id:"G"}, {_id:"H"}, {_id:"I"}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"A", _to:"C"}, {_from:"B", _to:"B"}, {_from:"B", _to:"D"}, {_from:"C", _to:"B"}, {_from:"C", _to:"D"}, {_from:"E", _to:"D"}, {_from:"E", _to:"F"}, {_from:"E", _to:"G"}, {_from:"E", _to:"H"}, {_from:"F", _to:"D"}, {_from:"G", _to:"D"}, {_from:"G", _to:"F"}, {_from:"I", _to:"A"}]);
Running on HDC Graphs
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: k_core
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
k |
Integer | ≥1 | / | No | Specifies the minimum degree k for nodes to be included in the k-core subgraph. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results; this option is only valid in File Writeback. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.k_core.write("my_hdc_graph", {
k: 3,
return_id_uuid: "id"
}, {
file: {
filename: "3-core"
}
})
algo(k_core).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
k: 3,
return_id_uuid: "id"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "3-core"
}
})
Result:
_id
G
F
E
D
Full Return
CALL algo.k_core.run("my_hdc_graph", {
k: 2
}) YIELD k2
RETURN k2
exec{
algo(k_core).params({
k: 2
}) as result
return result
} on my_hdc_graph
[{"id":"G","uuid":"13690943966717935617","schema":"default","values":{}}]
[{"id":"D","uuid":"288231475663339522","schema":"default","values":{}}]
[{"id":"F","uuid":"2882304861028745219","schema":"default","values":{}}]
[{"id":"B","uuid":"3530823207370096641","schema":"default","values":{}}]
[{"id":"E","uuid":"10520409829049106435","schema":"default","values":{}}]
[{"id":"C","uuid":"12033619303845593090","schema":"default","values":{}}]
Stream Return
CALL algo.k_core.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
k: 3
}) YIELD r
FOR node in r
RETURN node._id
exec{
algo(k_core).params({
k: 3
}).stream() as r
uncollect r as node
return node._id
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| node._id |
|---|
| G |
| D |
| F |
| E |
Running on Distributed Projections
Creating Distributed Projection
To project the entire graph to its shard servers as myProj:
CREATE PROJECTION myProj OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true
}
create().projection("myProj", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true
})
Parameters
Algorithm name: k_core
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
k |
Integer | ≥1 | / | No | Specifies the minimum degree k for nodes to be included in the k-core subgraph. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.k_core.write("myProj", {
k: 3
}, {
file: {
filename: "3-core"
}
})
algo(k_core).params({
projection: "myProj",
k: 3
}).write({
file: {
filename: "3-core"
}
})
_id
E
D
F
G

