Overview
The K-Hop All algorithm identifies the K-hop neighborhood of each node in the graph. This algorithm is widely used in scenarios such as relationship discovery, impact prediction, and friend recommendation.
The K-Hop All algorithm can be considered as the batch execution of the UQL K-Hop Query.
Considerations
Although the K-Hop All algorithm is optimized for high concurrency performance, it may demand substantial computational resources when applied to large graphs (those with tens of millions of nodes or edges), or graphs with numerous supernodes. To optimize performance, it is advisable to avoid performing K-Hop All calculation that is excessively deep, considering the specific characteristics and size of the graph being analyzed.
In graph G = (V, E), if |V|/|E|=100, querying the 5-hop neighbors of a node requires a theoretical computational complexity of 105 (equivalent to 10 billion computations), which would take approximately 100ms. Extrapolating from this, completing such a query in a graph with 10 million nodes would require 1 million seconds (equivalent to around 12 days). It's important to consider the computational demands and time requirements when working with graphs of this scale.
Example Graph
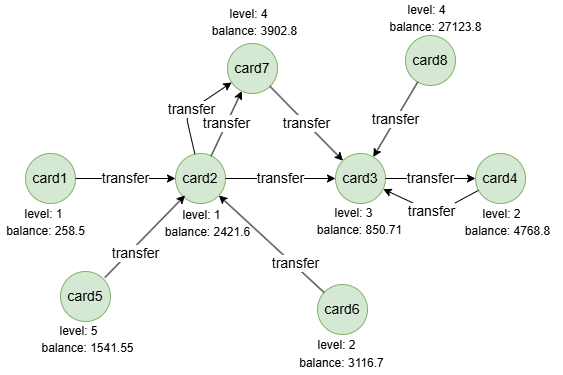
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
ALTER GRAPH CURRENT_GRAPH ADD NODE {
card ({level int32, balance double})
};
ALTER GRAPH CURRENT_GRAPH ADD EDGE {
transfer ()-[]->()
};
INSERT (card1:card {_id: "card1", level: 1, balance: 258.5}),
(card2:card {_id: "card2", level: 1, balance: 2421.6}),
(card3:card {_id: "card3", level: 3, balance: 850.71}),
(card4:card {_id: "card4", level: 2, balance: 4768.8}),
(card5:card {_id: "card5", level: 5, balance: 1541.55}),
(card6:card {_id: "card6", level: 2, balance: 3116.7}),
(card7:card {_id: "card7", level: 4, balance: 3902.8}),
(card8:card {_id: "card8", level: 4, balance: 27123.8}),
(card1)-[:transfer]->(card2),
(card2)-[:transfer]->(card3),
(card2)-[:transfer]->(card7),
(card2)-[:transfer]->(card7),
(card3)-[:transfer]->(card4),
(card4)-[:transfer]->(card3),
(card5)-[:transfer]->(card2),
(card6)-[:transfer]->(card2),
(card7)-[:transfer]->(card3),
(card8)-[:transfer]->(card3);
create().node_schema("card").edge_schema("transfer");
create().node_property(@card, "level", int32).node_property(@card, "balance", double);
insert().into(@card).nodes([{_id:"card1", level:1, balance:258.5}, {_id:"card2", level:1, balance:2421.6}, {_id:"card3", level:3, balance:850.71}, {_id:"card4", level:2, balance:4768.8}, {_id:"card5", level:5, balance:1541.55}, {_id:"card6", level:2, balance:3116.7}, {_id:"card7", level:4, balance:3902.8}, {_id:"card8", level:4, balance:27123.8}]);
insert().into(@transfer).edges([{_from:"card1", _to:"card2"}, {_from:"card2", _to:"card3"}, {_from:"card2", _to:"card7"}, {_from:"card2", _to:"card7"}, {_from:"card3", _to:"card4"}, {_from:"card4", _to:"card3"}, {_from:"card5", _to:"card2"}, {_from:"card6", _to:"card2"}, {_from:"card7", _to:"card3"}, {_from:"card8", _to:"card3"}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: khop_all
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ids |
[]_id |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies nodes for computation by their _id. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
uuids |
[]_uuid |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies nodes for computation by their _uuid. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
k_start |
Integer | ≥1 | 1 |
Yes | Specifies the starting depth for the K-Hop query, defining the querying depth range as [k_start, k_end]. |
k_end |
Integer | ≥1 | 1 |
Yes | Specifies the ending depth for the K-Hop query, defining the querying depth range as [k_start, k_end]. |
direction |
String | in, out |
/ | Yes | Specifies the direction of all edges in the shortest paths. |
node_property |
[]"<@schema.?><property>" |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies numeric node properties to perform aggregations. This option must be used with aggregate_opt. |
aggregate_opt |
[]String | max, min, mean, sum, var, dev |
/ | Yes | Specifies the types of aggregations to apply to the values of the specified node properties. This option must be used with node_property, with each aggregation type corresponding to one property. The aggregation types include:
|
src_include |
Integer | 0, 1 |
0 |
Yes | Whether to include the source node in the results; sets to 1 to include, or 0 to exclude. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
File Writeback
This algorithm can generate two files:
Spec |
Content |
|---|---|
filename_ids |
|
filename |
|
CALL algo.khop_all.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ["card1", "card7"],
k_start: 2,
k_end: 3,
direction: "out",
node_property: ["@card.level", "@card.balance"],
aggregate_opt: ["sum", "mean"]
}, {
file: {
filename_ids: "neighbors",
filename: "aggregations"
}
})
algo(khop_all).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ["card1", "card7"],
k_start: 2,
k_end: 3,
direction: "out",
node_property: ["@card.level", "@card.balance"],
aggregate_opt: ["sum", "mean"]
}).write({
file: {
filename_ids: "neighbors",
filename: "aggregations"
}
})
Results:
_id,_id
card1,card3
card1,card7
card1,card4
card7,card4
_id,sum,mean,count
card1,9,3174.1,3
card7,2,4768.8,1
DB Writeback
Writes the aggregation results (if any) and the count values to the specified node properties. The property type is double.
CALL algo.khop_all.write("my_hdc_graph", {
k_start: 2,
k_end: 2,
node_property: ["@card.level", "@card.level", "@card.balance"],
aggregate_opt: ["sum", "mean", "mean"]
}, {
db: {
property: "khop2"
}
})
algo(khop_all).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
k_start: 2,
k_end: 2,
node_property: ["@card.level", "@card.level", "@card.balance"],
aggregate_opt: ["sum", "mean", "mean"]
}).write({
db: {
property: "khop2"
}
})
The aggregation results are written to new properties sum, mean and mean1; the count values are written to the new property khop2.
Full Return
CALL algo.khop_all.run("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ["card1", "card7"],
k_start: 2,
k_end: 3,
node_property: ["@card.level", "@card.balance"],
aggregate_opt: ["max", "mean"]
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(khop_all).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ["card1", "card7"],
k_start: 2,
k_end: 3,
node_property: ["@card.level", "@card.balance"],
aggregate_opt: ["max", "mean"]
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _id | max | mean | count |
|---|---|---|---|
| card1 | 5 | 6884.06 | 6 |
| card7 | 5 | 7361.87 | 5 |
Stream Return
CALL algo.khop_all.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: "card2",
k_start: 2,
k_end: 2,
node_property: ["@card.level", "@card.balance"],
aggregate_opt: ["max", "max"]
}) YIELD results
RETURN results
exec{
algo(khop_all).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: "card2",
k_start: 2,
k_end: 2,
node_property: ["@card.level", "@card.balance"],
aggregate_opt: ["max", "max"]
}).stream() as results
return results
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _id | max | max1 | count |
|---|---|---|---|
| card2 | 4 | 27123.8 | 2 |

