Overview
The Triangle Counting algorithm identifies triangles in a graph, where each triangle consists of three mutually connected nodes. Triangles indicate the presence of loops and strong connectivity patterns, making them important for graph structure analysis.
In social networks, triangles indicate cohesive communities, helping to reveal clustering and interconnectedness of individuals or groups within the network. In financial or transaction networks, triangles may signal suspicious or fraudulent behavior. Triangle counting aids in detecting potential patterns of collusion or tightly linked transactions that might require further investigation.
Concepts
Triangle
In a complex graph, multiple edges may exist between two nodes, which can lead to the formation of more than one triangle involving three nodes. Take the graph below as an example:
- When counting triangles formed by edges, there are 4 distinct triangles.
- When counting triangles formed by nodes, there are 2 distinct triangles.

In complex graphs, the number of triangles formed by edges often exceeds that formed by nodes. The choice of assembly principle should align with the objectives of the analysis and the insights intended to be derived from the graph data. In social network analysis, where the focus is often on connectivity patterns among individuals, the node-based assembly principle is commonly adopted. In financial network analysis or other similar domains, the edge-based assembly principle is often preferred. Here, the emphasis is on the relationships between nodes, such as financial transactions or interactions. Assembling triangles based on edges allows for the examination of how tightly nodes are connected and how funds or information flow through the network.
Considerations
- The Triangle Counting algorithm treats all edges as undirected, ignoring their original direction.
Example Graph
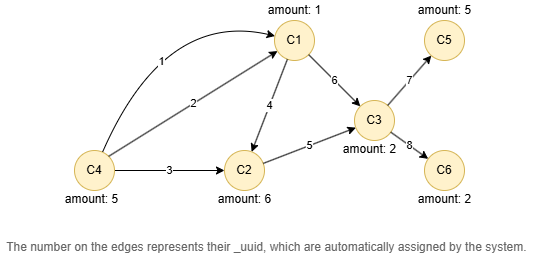
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
AALTER NODE default ADD PROPERTY {
amount int32
};
INSERT (C1:default {_id: "C1", amount: 1}),
(C2:default {_id: "C2", amount: 6}),
(C3:default {_id: "C3", amount: 2}),
(C4:default {_id: "C4", amount: 5}),
(C5:default {_id: "C5", amount: 5}),
(C6:default {_id: "C6", amount: 2}),
(C4)-[:default]->(C1),
(C4)-[:default]->(C1),
(C4)-[:default]->(C2),
(C1)-[:default]->(C2),
(C2)-[:default]->(C3),
(C1)-[:default]->(C3),
(C3)-[:default]->(C5),
(C3)-[:default]->(C6);
create().node_property(@default, "amount", int32);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"C1", amount: 1}, {_id:"C2", amount: 6}, {_id:"C3", amount: 2}, {_id:"C4", amount: 5}, {_id:"C5", amount: 5}, {_id:"C6", amount: 2}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"C4", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"C4", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"C4", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"C1", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"C2", _to:"C3"}, {_from:"C1", _to:"C3"}, {_from:"C3", _to:"C5"}, {_from:"C3", _to:"C6"}]);
Running on HDC Graphs
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: triangle_counting
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
type |
Integer | 1, 2 |
1 |
Yes | Set to 1 to assemble triangles by edges, or 2 to assemble triangles by nodes. |
result_type |
Integer | 1, 2 |
1 |
Yes | Set to 1 to return the number of triangles, or 2 to return nodes or edges in each triangle. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. Edges can only be represented by _uuid. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.triangle_counting.write("my_hdc_graph", {
type: 1,
result_type: 2
}, {
file: {
filename: "byEdges"
}
})
algo(triangle_counting).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
type: 1,
result_type: 2
}).write({
file: {
filename: "byEdges"
}
})
Result:
_edge_uuids
1,3,4
2,3,4
6,5,4
CALL algo.triangle_counting.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
type: 2,
result_type: 2
}, {
file: {
filename: "byNodes"
}
})
algo(triangle_counting).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
return_id_uuid: "id",
type: 2,
result_type: 2
}).write({
file: {
filename: "byNodes"
}
})
Result:
_node_ids
C1,C4,C2
C1,C3,C2
Stats Writeback
CALL algo.triangle_counting.write("my_hdc_graph", {}, {
stats: {}
})
algo(triangle_counting).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph"
}).write({
stats: {}
})
Result:
| triangle_count |
|---|
| 3 |
Full Return
CALL algo.triangle_counting.run("my_hdc_graph", {
result_type: 1
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(triangle_counting).params({
result_type: 1
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| triangle_count |
|---|
| 3 |
Stream Return
CALL algo.triangle_counting.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
type: 2,
result_type: 2
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(triangle_counting).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
type: 2,
result_type: 2
}).stream() as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _ids |
|---|
| ["C1","C4","C2"] |
| ["C1","C3","C2"] |
Stats Return
CALL algo.triangle_counting.stats("my_hdc_graph", {
result_type: 1
}) YIELD stats
RETURN stats
exec{
algo(triangle_counting).params({
result_type: 1
}).stats() as stats
return stats
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| triangle_count |
|---|
| 3 |
Running on Distributed Projections
Creating Distributed Projection
To project the entire graph to its shard servers as myProj:
CREATE PROJECTION myProj OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true
}
create().projection("myProj", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true
})
Parameters
Algorithm name: triangle_counting
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
result_type |
Integer | 1, 2 |
1 |
Yes | Sets to 1 to return the number of triangles, or 2 to return nodes or edges in each triangle. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned; -1 includes all results. |
The distributed version of this algorithm only supports identifying triangles by nodes in the graph.
File Writeback
CALL algo.triangle_counting.write("myProj", {
result_type: 1
}, {
file: {
filename: "triCnt"
}
})
algo(triangle_counting).params({
projection: "myProj",
result_type: 1
}).write({
file: {
filename: "triCnt"
}
})
triangle
2
CALL algo.triangle_counting.write("myProj", {
result_type: 2
}, {
file: {
filename: "triNodes"
}
})
algo(triangle_counting).params({
projection: "myProj",
result_type: 2
}).write({
file: {
filename: "triNodes"
}
})
triangle
216173881625411585,3386708019294240770,13330655996528295937
216173881625411585,10088064264821538817,13330655996528295937
The results utilize nodes'
_uuidvalues.

