Overview
Graph traversal is a search technique used to systematically visit and explore all the nodes in a graph. Its primary goal is to reveal and examine the structure and connections of the graph. There are two common strategies for graph traversal:
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
- Depth-First Search (DFS)
The Breadth-First Search (BFS) algorithm explores a graph level by level and proceeds as follows:
- Create a queue (first in, first out) to keep track of visited nodes.
- Start from a selected node, enqueue it into the queue, and mark it as visited.
- Dequeue a node from the front of the queue, enqueue all its unvisited neighbors into the queue and mark them as visited.
- Repeat step 3 until the queue is empty.
The following example demonstrates BFS traversal starting from node A, assuming neighbors are visited in alphabetical order (A–Z):
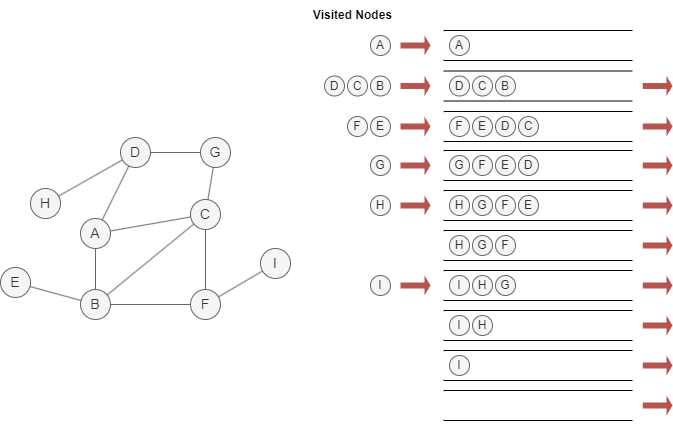
Considerations
- Only nodes within the same connected component as the start node will be traversed. Nodes in other connected components are excluded from the traversal results.
Example Graph
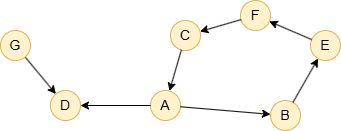
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
INSERT (A:default {_id: "A"}),
(B:default {_id: "B"}),
(C:default {_id: "C"}),
(D:default {_id: "D"}),
(E:default {_id: "E"}),
(F:default {_id: "F"}),
(G:default {_id: "G"}),
(A)-[:default]->(B),
(A)-[:default]->(D),
(B)-[:default]->(E),
(C)-[:default]->(A),
(E)-[:default]->(F),
(F)-[:default]->(C),
(G)-[:default]->(D);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"}, {_id:"B"}, {_id:"C"}, {_id:"D"}, {_id:"E"}, {_id:"F"}, {_id:"G"}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"G", _to:"D"}, {_from:"A", _to:"D"}, {_from:"A", _to:"B"}, {_from:"B", _to:"E"}, {_from:"E", _to:"F"}, {_from:"F", _to:"C"}, {_from:"C", _to:"A"}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: traverse
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ids |
_id |
/ | / | No | Specifies the node to start traversal by its _id. |
uuids |
_uuid |
/ | / | No | Specifies the node to start traversal by its _uuid. |
direction |
String | in, out |
/ | Yes | Specifies to traverse through only incoming edges (in) or outgoing edges (out). |
traverse_type |
String | bfs |
bfs |
Yes | To traverse the graph in the BFS fashion, keep it as bfs. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.traverse.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['A'],
direction: 'out',
traverse_type: 'bfs'
}, {
file: {
filename: "visited_nodes"
}
})
algo(traverse).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['A'],
direction: 'out',
traverse_type: 'bfs'
}).write({
file: {
filename: "visited_nodes"
}
})
Result:
node,parent
D,A
F,E
B,A
A,A
E,B
C,F

