Overview
The Connected Component algorithm identifies the connected components in a graph, which is the essential indicator to examine the connectivity and topology characteristics of the graph.
The number of connected components in a graph can serve as a coarse-grained metering method. If the number of connected components remains unchanged after certain operations or modifications to the graph, it suggests that the macroscopic connectivity and topology characteristics of the graph have not been altered significantly.
This information is valuable in various graph analysis scenarios. For example, in social networks, if the number of connected components remains the same over time, it implies that the overall connectivity patterns and community structures within the network have not experienced substantial changes.
Concepts
Connected Component
A connected component is a maximal subset of nodes in a graph where all nodes in that subset are reachable from one another by following edges in the graph. A maximal subset means that no additional nodes can be added to the subset without breaking the connectivity requirement.
The number of connected components in a graph indicates the level of disconnectedness or the presence of distinct subgraphs within the overall graph. A graph with exactly one connected component encompassing all nodes is called a connected graph.
Weakly and Strongly Connected Component
There are two important concepts related to connected component: weakly connected component (WCC) and strongly connected component (SCC):
- A WCC is a subset of nodes in a directed or undirected graph where a path exists between any pair of nodes when edge directions are ignored.
- An SCC is a subset of nodes in a directed graph where there is a directed path between every pair of nodes. In other words, for any two nodes u and v in an SCC, there exists a directed path from u to v and from v to u. All edges along these paths follow the same direction.
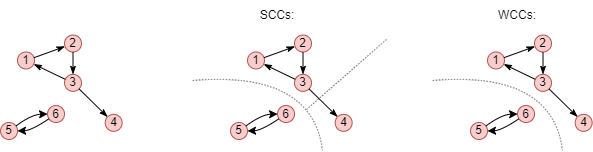
This example shows the 3 strongly connected components and 2 weakly connected components of a graph. The number of SCCs in a graph is always equal to or greater than the number of WCCs, since SCCs impose stricter connectivity conditions than WCCs.
Considerations
- Each isolated node in the graph constitutes a connected component and is considered both a strongly connected component and a weakly connected component.
Example Graph
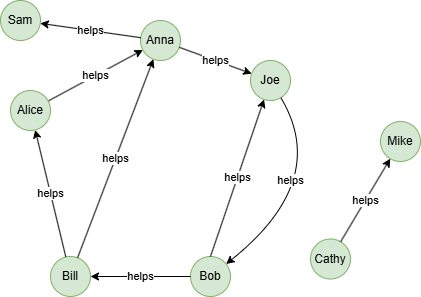
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
ALTER GRAPH CURRENT_GRAPH ADD NODE {
member ()
};
ALTER GRAPH CURRENT_GRAPH ADD EDGE {
helps ()-[]->()
};
INSERT (Mike:member {_id: "Mike"}),
(Cathy:member {_id: "Cathy"}),
(Anna:member {_id: "Anna"}),
(Joe:member {_id: "Joe"}),
(Sam:member {_id: "Sam"}),
(Bob:member {_id: "Bob"}),
(Bill:member {_id: "Bill"}),
(Alice:member {_id: "Alice"}),
(Cathy)-[:helps]->(Mike),
(Anna)-[:helps]->(Sam),
(Anna)-[:helps]->(Joe),
(Joe)-[:helps]->(Bob),
(Bob)-[:helps]->(Joe),
(Bob)-[:helps]->(Bill),
(Bill)-[:helps]->(Alice),
(Bill)-[:helps]->(Anna),
(Alice)-[:helps]->(Anna);
create().node_schema("member").edge_schema("helps");
insert().into(@member).nodes([{_id:"Mike"}, {_id:"Cathy"}, {_id:"Anna"}, {_id:"Joe"}, {_id:"Sam"}, {_id:"Bob"}, {_id:"Bill"}, {_id:"Alice"}]);
insert().into(@helps).edges([{_from:"Cathy", _to:"Mike"}, {_from:"Anna", _to:"Sam"}, {_from:"Anna", _to:"Joe"}, {_from:"Joe", _to:"Bob"}, {_from:"Bob", _to:"Joe"},{_from:"Bob", _to:"Bill"}, {_from:"Bill", _to:"Alice"}, {_from:"Bill", _to:"Anna"}, {_from:"Alice", _to:"Anna"}]);
Running on HDC Graphs
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: connected_component
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
cc_type |
Integer | 1, 2 |
1 |
Yes | Specifies the type of connected component to identify. Set to 1 for WCC, or 2 for SCC. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
order |
String | asc, desc |
/ | Yes | Sorts the results by count; this option is only valid in Stream Return when mode is set to 2. |
In the results of this algorithm, each connected component is represented by the same community_id, which corresponds to the _uuid value of one of its nodes.
File Writeback
This algorithm can generate three files:
Spec |
Content |
|---|---|
filename_community_id |
|
filename_ids |
|
filename_num |
|
CALL algo.connected_component.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
cc_type: 1
}, {
file: {
filename_community_id: "f1",
filename_ids: "f2",
filename_num: "f3"
}
})
algo(connected_component).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
return_id_uuid: "id",
cc_type: 1
}).write({
file: {
filename_community_id: "f1",
filename_ids: "f2",
filename_num: "f3"
}
})
Result:
_id,community_id
Alice,0
Cathy,1
Anna,0
Bob,0
Joe,0
Bill,0
Mike,1
Sam,0
community_id,_ids
0,Alice;Anna;Bob;Joe;Bill;Sam;
1,Cathy;Mike;
community_id,count
0,6
1,2
DB Writeback
Writes the community_id values from the results to the specified node property. The property type is uint32.
CALL algo.connected_component.write("my_hdc_graph", {}, {
db: {
property: "wcc_id"
}
})
algo(connected_component).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph"
}).write({
db: {
property: "wcc_id"
}
})
Stats Writeback
CALL algo.connected_component.write("my_hdc_graph", {}, {
stats: {}
})
algo(connected_component).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph"
}).write({
stats: {}
})
Result:
| community_count |
|---|
| 2 |
Full Return
CALL algo.connected_component.run("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
cc_type: 2
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(connected_component).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
cc_type: 2
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _id | community_id |
|---|---|
| Alice | 0 |
| Cathy | 1 |
| Anna | 0 |
| Bob | 0 |
| Joe | 0 |
| Bill | 0 |
| Mike | 6 |
| Sam | 7 |
Stream Return
This Stream Return supports two modes:
| Item | Spec | Columns |
|---|---|---|
mode |
1 (Default) |
|
2 |
|
CALL algo.connected_component.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
cc_type: 2
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(connected_component).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
cc_type: 2
}).stream() as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _id | community_id |
|---|---|
| Alice | 0 |
| Cathy | 1 |
| Anna | 0 |
| Bob | 0 |
| Joe | 0 |
| Bill | 0 |
| Mike | 6 |
| Sam | 7 |
CALL algo.connected_component.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
cc_type: 2,
order: "asc"
}, {
mode: 2
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(connected_component).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
cc_type: 2,
order: "asc"
}).stream({
mode: 2
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| community_id | count |
|---|---|
| 6 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 |
| 0 | 5 |
Stats Return
CALL algo.connected_component.stats("my_hdc_graph", {}) YIELD wcc_count
RETURN wcc_count
exec{
algo(connected_component).params().stats() as wcc_count
return wcc_count
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| community_count |
|---|
| 2 |
Running on Distributed Projections
Creating Distributed Projection
To project the entire graph to its shard servers as myProj:
CREATE PROJECTION myProj OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true
}
create().projection("myProj", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true
})
Parameters
Algorithm name: wcc
The algorithm does not require any parameters.
The distributed version of this algorithm supports identifying only weakly connected components (WCC) in the graph. In the results of this algorithm, each connected component is represented by the same community_id.
File Writeback
CALL algo.wcc.write("myProj", {}, {
file: {
filename: "wcc"
}
})
algo(wcc).params({
projection: "myProj"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "wcc"
}
})
Result:
_id,community_id
Anna,4827860999564427272
Joe,4827860999564427272
Sam,4827860999564427272
Mike,6413128068398841858
Bill,4827860999564427272
Cathy,6413128068398841858
Alice,4827860999564427272
Bob,4827860999564427272
DB Writeback
Writes the community_id values from the results to the specified node property. The property type is uint64.
CALL algo.wcc.write("myProj", {}, {
db: {
property: "wcc_id"
}
})
algo(wcc).params({
projection: "myProj"
}).write({
db: {
property: "wcc_id"
}
})

